All the e-devices, such as computers, mobile phones, and other connected devices, communicate via IP (internet protocol) addresses (IPV4 and IPV6). As the Internet Protocol is pretty challenging and complex for human beings or end-users to remember, they need to enter the correct IP addresses in the search boxes of their browsers. In simple words, remembering your friend’s contact number is tough, but remembering his name is easy, and the name of your friend is nothing but a domain name. To reduce complexity, the term “domain name” was coined.
Wondering what is AWS Route 53 and why it’s crucial for modern cloud infrastructure? Amazon Route 53 is a scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service from AWS, designed to route end users to internet applications reliably. It supports domain registration, health checks, and traffic management. Whether you’re a beginner trying to understand what is Route 53 in AWS or a professional exploring Route 53 AWS use cases, this guide is for you. To master concepts like AWS Rout 53, enroll in our AWS Online Certification Training and accelerate your cloud journey with 3RI Technologies.
The “domain name service” is mapping IP addresses to domain names that allow end users to find and access their desired websites or servers using the domain name. In this article, you will learn about Amazon Web Services (AWS) Route 53, a subsidiary of the world’s biggest tech giant, Amazon.com. So, let’s get started and learn more about Route 53, its workings, features, and methodologies. Before moving to all these sections, let’s begin with the definition of AWS Route 53.
Understanding Amazon Route 53: AWS DNS Service Made Simple
The acronym for AWS is Amazon Web Services, a subsidiary of tech giant Amazon.com. It efficiently provides cloud computing platforms to organizations of all sizes. Individuals, MNCs, small businesses, startups, and governments use AWS to complete tasks without paying a fee (I would say a subscription).
Amazon Route 53 is a highly scalable cloud Domain Name System (DNS) web service, beautifully created for developers and corporations to route end users to Internet apps (mobile or web applications). It converts complex IP addresses into easy-to-understand and readable names.
Furthermore, the prime task of AWS Route 53 is to manage DNS for machines that are deployed or running on the Amazon Cloud (virtual storage). AWS Route 53 efficiently connects end-user requests to EC2 instances, S3 buckets, load balancers, etc. Additionally, AWS end-users are directed to infrastructure outside of AWS with the help of AWS Route 53.
Interested to begin a career in AWS? Enroll now for AWS Training in Pune.
How does AWS Route 53 function?
Amazon Web Services Route 53 bridges the internet traffic to dedicated servers, which would be responsible for hosting the web application. Through the AWS Management Console, the subscription-based AWS capability allows end customers to register domain names and undertake infrastructure health checks without the need for any coding experience. Let’s move ahead and learn what AWS Route 53 is and how it works for better understanding.
Follow the below-shared steps to know how AWS makes Route 53 work:
- First of all, the domain name gets registered with AWS Route 53. Following registration, it is configured to direct Internet traffic to the domain name’s servers.
- Now, the AWS end-users feed the domain name into the search bar.
- The Internet service provider then routes the request to a DNS resolver. A DNC resolver is a program that converts a domain name into its corresponding IP address.
- After that, the DNS resolver sends the user request to a DNS root name server, and then it gets directed to its top-level domain (TLD) server, and at the end, it moves to AWS Route 53.
- After reaching the ultimate level, AWS Route 53, the Route 53 name server returns the IP address of the domain name to the DNS resolver.
- Now that the DNC resolver has the desired IP address, it sends the end AWS user request to the correct server, which will host it as per the configuration.
Furthermore, the best part of using AWS Route 53 is that it examines the health conditions of servers working in the backend. The Domain Name Server (DNS) evaluates the availability of endpoints; if found weak or unworthy, AWS ultimately routes the traffic to another robust endpoint and raises the alarm for quick actions.

Methodologies related to Route 53
- Records: Records are developed to route internet traffic to endpoints. It figures out, or in other words, it amazingly identifies which route is best so that the Internet traffic is best routed for a domain name and reaches the final resources or endpoints.
- Hosted zone: Following domain name registration, AWS Route53 creates a public hosted zone with the same name as the domain name. A “hosted zone” is nothing more than a collection of records that contains information about how to route the internet traffic of its domains and all their subdomains.
- DNS query: A DNS query is a request for information directly sent from the DNS client to the DNS server.
- Alias records: The top DNS namespace node creates alias records, which help direct Internet traffic to AWS endpoints like S3 buckets, CloudFront, etc.
- Name servers: The DNS name servers that transform a domain name into an IP address are known as name servers. In such a fashion, traffic on the Internet can be redirected to other dependable, exceptionally healthy resources.
- DNS failover: The DNS failover mechanism is implemented whenever a problem with the route is found. It is a frequently used strategy to divert Internet traffic from destructive to favorable resources.
- Routing policy: Routing policy determines how Amazon Web Services (AWS) Route53 acknowledges queries by AWS end-users.
Enroll in our AWS Online Training today!
From where is the name Route 53 derived?
Undoubtedly, the IT world has evolved immensely. Businesses, big or small, are all using the Internet to boost their revenue and spread their business on a global level. To execute the Internet work, IP (Internet Protocols) addresses are the prime link that are used to make connections between two or more systems.
IP addresses play a major role and cater to websites, e-devices (laptops and PCs), and other devices that work on the Internet to ensure smooth communication and a robust network.
“Route” in Route 53 is derived most probably from the U.S. Routes. It is a United States-numbered highway system. “53” is a port referenced to the TCP/UDP port 53. It is widely used to locate Domain Name Server requests.
Now another query arises: What is this DNS?
The full form of the DNS is Domain Name System. It is nothing but a translator device that converts names into IP addresses. In simple words, DNS is the home of servers, which includes worldwide servers. DNS (Domain Name System) is like a bridge that helps e-devices talk with other devices. DNS translates easy-to-understand names like Google.com into numbers (IP addresses) that are tough to remember.
Types of routing policies associated with AWS Route 53
- Simple routing policy: The “simple routing policy” in AWS Route 53 is nothing but a simple Route 53 routing method used to route internet traffic to a single resource.
- Failover routing policy: one of the best routing policies associated with AWS Route 53 is the failover routing policy. Under the failover routing policy, whenever a resource seems unhealthy or in the worst possible conditions, the following routing policy helps route the internet traffic from unhealthy endpoints to healthy endpoints or healthy resources.
- Geolocation routing policy: Under the geolocation routing policy, internet traffic gets routed to different resources based on the geographic location of the AWS end-user. Here, the geographic location can be set by country, state, area, region, etc.
- Latency routing policy: To host a website in multiple regions, the Latency routing policy comes in use. Latency routing policy assists in serving requests from the Aws region that tremendously offers the lowest latency and boosts performance for the AWS end-users.
- Multivalue routing policy: Multivalue routing policy is yet another crucial routing policy associated with Aws route 53. Multivalue routing policy comes in use when the Aws end-user wants Aws Route 53 to return multiple values in reply to Domain Name Serve 9DNS) queries. The multivalue routing policy examines the health of endpoints and resources and returns multiple values for healthy endpoints and resources.
- Weighted routing policy: The weighted routing policy efficiently routes Internet traffic to multiple resources within a single domain name based on the ratio opted by the AWS end-user.
Features of AWS Route 53
- Highly reliable: AWS Route 53’s dispersed architecture toward DNS servers aids in maintaining a continuous ability to route applications to end users.
- Scalable: AWS Route 53 can efficiently tackle vast volumes of queries without the end user’s interaction.
- Compatible: AWS Route 53 can efficiently work with other AWS services and can be easily used to map domain names to EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and other AWS services.
- Handy to use: The AWS Route 53 is easy to use. The end AWS user can quickly sign up, easily configure DNS settings, and offers quick response to DNS queries.
- Health Check: AWS Route 53 examines the health condition of the application, and if any issue gets detected, then AWS Route 53 automatically redirects the end users to much more healthy endpoints for a better experience.
- Cost-Effective: Using AWS has perks; here, AWS users will have to pay for what they would use. Payment will be made as per the services the end-users have opted for. Additionally, features like traffic policies and health checks are available at a minimal service cost.
- Secure: The AWS Route 53 is super secure, as there is complete control over each AWS end user with the AWS account. How? by integrating Route 53 with AWS (IAM), which decides which user has the right to access which section of Route 53. It is highly authenticated, providing its permission to access only authorized users.
- User-Friendly DNS Management: AWS Route 53 offers a straightforward and user-friendly interface for managing Domain Name System (DNS) settings. The platform provides a seamless experience, and end-users can easily register new domains and configure DNS records.
- Traffic Flow Management: Route 53 has a traffic flow management feature, through which users can easily control the flow of traffic to their applications.
- Cost-Effective Pricing Model: AWS Route 53 provides users with an amazing cost-effective pricing model in which users are required to pay only for the resources they are willing to use.
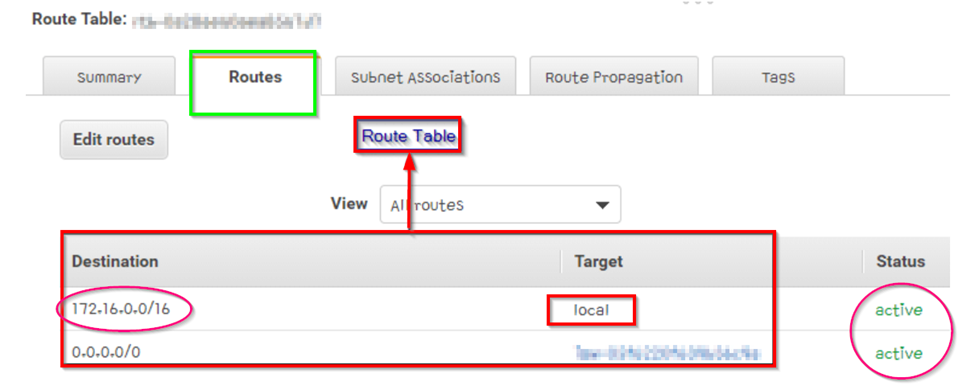
AWS route tables
It is a set of rules that say where the network traffic is leading. It is a major part of the AWS environment. All the subnets in the AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) must be connected to an AWS route table. The table takes complete control of routing for those particular subnets. It contains information such as the linked VPC’s “The ID” and the Route Table ID. AWS route tables have a target and a destination IP address.
Does VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer offer Route 53 monitoring capabilities?
VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer (formerly Avi Networks) does not have native integration with Amazon Route 53 for monitoring capabilities. While NSX ALB (Advanced Load Balancer) excels in application delivery and load balancing, users typically leverage Route 53 for DNS management and resolution within the AWS ecosystem. However, for monitoring, users might need to employ additional tools or scripts to integrate NSX ALB with Route 53 effectively.
The VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer provides businesses with full-featured algorithms for load balancing, automation, and security, like DDoS, monitoring, and multi-cloud load balancing.
For more Trending and Job-Oriented courses check 3RI Technologies
How does the AWS Route 53 service work for routing traffic between end-users and the hosted web apps?
AWS Route 53 is like a guide in the Internet world; it instructs, or can be said to guide, the end-users to the right destination whenever they enter a web address into their browsers.
I guess if you are thinking of a road trip and require a road map, then my friend Route 53 is the GPS that helps users find their way to your hosted web app.
Here’s how it works:
- Domain Registration: Just like you get a unique license plate for your car, you register a unique domain name for your website, like www.yourwebsite.com. Route 53 helps you manage and register these domain names.
- DNS (Domain Name System): DNS is something like a warehouse of the Internet. When someone types your web address into their browser, Route 53 translates that human-friendly name into an IP address, which is a unique number that identifies your web server on the internet.
- Routing Traffic: Now, imagine your website is hosted on different servers with distinct geographic sites. Route 53 decides which server is closest to the user making the request. It’s like finding the nearest restaurant when you’re hungry rather than driving across town.
- Health Checks: Route 53 is like a vigilant friend who constantly checks if your servers are healthy. If one server is down, it will redirect traffic to a healthy server so users don’t encounter any roadblocks.
- Traffic Policies: Suppose you have different versions of your website or want to distribute traffic in a specific way. Route 53 lets you set rules and policies, like sending more traffic to a new feature you just launched.
- Scalability: As your website grows, Route 53 scales with you. It handles more users like a well-designed highway that can accommodate more traffic without causing congestion.
So, in simple terms, AWS Route 53 is a smart guide that helps end-users find websites, ensures they reach them quickly and reliably, and even adapts to changes along the way.
Route 53 Resolver for Hybrid Clouds
Amazon Route 53 Resolver is a powerful service that addresses the challenges encountered in hybrid cloud environments where private centers are merged with Amazon VPCs using managed VPNs or AWS Direct Connect. In such scenarios, efficient DNS resolution is crucial for smooth communication between on-site resources and Amazon VPC servers.
The typical issue faced in this setup is the failure of lookups across the connection established between the private cloud and the user’s VPC. This disruption can lead to complications in routing requests. However, Amazon Route 53 Resolver provides an effective solution to enhance DNS resolution in hybrid cloud environments.
By leveraging Amazon Route 53 Resolver, users can overcome the lookup challenges by efficiently managing DNS queries between their on-premises DNS servers and Amazon VPC servers.
One key advantage of Amazon Route 53 Resolver is that DNS resolution happens transparently and efficiently across the hybrid cloud environment. Route 53 Resolver supports outbound communication from the VPC to the data center. It also performs inbound communication from an on-site source to the VPC.
This bidirectional capability ensures that DNS queries are resolved accurately, facilitating smooth communication between resources in the private center and the Amazon VPC.
Amazon Route 53 Limitations
There is no doubt that Amazon Route 53 is a powerful DNS service with state-of-the-art qualities. But every coin has two faces; likewise, the Amazon Route 53 comes with some limitations. Here are some limitations that you must understand:
- No DNSSEC support: the full form of DNSSEC Domain Name System Security Extensions. It has extensions used by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). DNSSEC is popularly used to secure the data exchanged in domain name systems on IP networks, but the sad part is that it is not supported by AWS Route 53.
- Forwarding options: Another limitation of Route 53 is the forwarding options. Route 53 does not support for forwarding or conditional forwarding options.
- Single Point of Failure: As Amazon Route 53 is combined with other AWS services, This can become a pain point for end-users and becomes a prime problem for AWS Route 53 disaster recovery.
- Limited Route 53 DNS load balancing: Route 53 has a limited DNS load balancing. The AWS Route 53 load balancer does not provide enterprise-level features. It is dedicated to offering basic load-balancing capabilities.
- Route 53 costs: Costing is another issue that might be a problem for end users. As businesses using Route 53 services with non-AWS endpoints, the service cost is pretty high (expensive).
- Zone Transfers: Route 53 being registered as a root level domain; DNS is not a reliable source for cloudwebsites.com.
AWS Route 53 Alternatives:
The IT world has been developing continuously, offering a variety of solutions to the same problem. AWS Route 53 is a biproduct of tech giant Amazon and is opted by multiple businesses to gain optimal solutions. But there are many other service providers who are into the same business, facilitating end-users with remarkable services based on parameters like integration, contracting, ease of deployment, and other related services. Some potential AWS Route 53 alternatives are shared below:
- Google Cloud DNS: Google Cloud DNS is a reliable alternative to AWS Route 53. It offers a domain name system, i.e., DNS services, focusing primarily on scalability. It offers a high-performance DNS solution with low latency, making it ideal for all kinds of businesses. It easily integrates with other Google cloud services, providing efficient cloud infrastructure.
- Microsoft Azure DNS: Microsoft Azure DNS is a robust DNS service that gives tough competition to AWS Route 53. It operates on the Azure cloud platform, offering highly secure DNS hosting services. It also provides features like traffic management and private DNS zones.
- Cloudflare DNS: Cloudflare DNS is a widely adopted alternative that focuses primarily on security and performance. Cloudflare’s DNS service ensures fast and secure resolution of domain names. It also facilitates businesses with added security features such as DDoS protection and an integrated web application firewall (WAF).
- Namecheap: Namecheap is a user-friendly alternative to AWS Route 53. It is widely acknowledged for being simple and minimally expensive. It offers domain registration and DNS management tools, that makes it an ideal option for all types of businesses. Namecheap offers services at a minimal cost, making it a budget-friendly option for businesses for domain management.
Bottom-line:
With the help of AWS Route 53, businesses can efficiently monitor and route global data traffic. In a nutshell, AWS route 53 is primarily used for DNS registration, routing internet traffic, and examining health status. Through AWS Route 53, one can create and handle their public domain name server (DNS) data. Additionally, Amazon Web Services lets you improve the performance and health of your application along with providing web servers and other essential resources.
You now understand what Amazon Route 53 is. So, if your website needs a name, go for AWS Route 53.
AWS Training Offered In Other Locations Are:




