How to become a Cloud Engineer?
What Is Cloud Computing?
In the Cloud, computer system resources (including data storage and computer power), in particular on-demand, are accessible without user direct active management. The term is widely used to describe data centers for many Internet users. The vast clouds, which predominate today, also have features spread from many central server locations. The edge server may be designated if the user link is relatively close.
Clouds can be restricted to a single entity (company clouds) or accessed by several (public Cloud).
Cloud computing depends on resource sharing to achieve efficiency and size savings.
Public and hybrid cloud proponents note that cloud computing enables enterprises to prevent or minimize upstream IT infrastructure costs. Proponents further argue that cloud computing provides businesses with quicker execution of their applications, better management, decreased maintenance, and enables IT teams to adapt resources faster to meet fluctuating and unpredictable demand. This means that burst computing capacity is high at certain peak demand times.
Cloud providers typically use a “pay-as-you-go” model to lead to unintended operating costs if administrators don’t know about cloud pricing models.
In 2019, Linux was the most commonly used operating system, including Microsoft’s services. It was thus classified as the dominant Cloud, the most common operating system, and the provision of high-capacity networks, low-cost computers, and storage devices. The availability of hardware virtualism, service-oriented architecture, and autonomous and utility computing contributed to an increase in Cloud computers.
How To Become A Cloud Engineer?
At least a bachelor’s in information technology, IT, or engineering is usually a cloud engineer. It is ideal to have a computer-related field certificate because this indicates that the future cloud engineer is aware of all the essential elements, including databases and network protection. It also means the engineers are aware of all forms of network technologies.
Cloud engineers typically experience IT systems between 5 and 10 years. Often they come from tech-related professions, including computer system analysts and database managers.
Certification or certification of a cloud engineer is not mandatory, but it demonstrates a commitment to integrity by keeping a voluntary certification. Individual cloud providers typically supply certificates to the company that the engineer works with.
Cloud Service Providers
Google Cloud Platform

The Cloud Google Platform (GCP) is an internally used cloud computing services series, including Google Search, Gmail, and File Storage, for its end users. Modular Cloud services are offered in combination with various management resources, including computing, data storage, data processing, and computer education. For registration, you must have a credit card or bank account information.
Google Cloud Platform includes infrastructure as a service, a service network, and a serverless computer environment.
In April 2008, Google announced App Engine, the company’s first cloud computing service, as a platform for developing and hosting Internet applications in Google-managed data centers. In November 2011, the service was commonly offered. Google has added various cloud services to the platform since the app engine was announced.
You can explore your knowledge with the help of GCP Online Training.
Features of Google Cloud Platform
- Cloud Infrastructure
- Data & Analytics
- Managed Computing
- Scalable Environment
- Layered Security
The Cloud Google Platform (GCP) is an internally used cloud computing services series, including Google Search, Gmail, and File Storage, for its end users. Modular Cloud services are offered in combination with various management resources, including computing, data storage, data processing, and computer education. For registration, you must have a credit card or bank account information.
Google Cloud Platform includes infrastructure as a service, a service network, and a serverless computer environment.
In April 2008, Google announced App Engine, the company’s first cloud computing service, as a platform for developing and hosting Internet applications in Google-managed data centers. In November 2011, the service was commonly offered. Google has added various cloud services to the platform since the app engine was announced.
How does Google Cloud work?
On Google Cloud Platform, web-based deployment and operations are supported with machine software. Its specialty provides individuals and organizations with the ability to develop, manage, and connect network applications. Consider tens of thousands of web sites running across a network of data centers, and you’ll get a primary photo.
Google tracks all the services that it uses, particularly how much power it consumes when using a website or an app or service on Google’s cloud platform (GC) for storage and database requests and network access. The cost per second for either tool (competitors charge per minute) is usually used by a website provider, with discounts if your services are generally used on the web by your clients instead of renting a server or DNS address per month.
The cloud platform of Google has some advantages.
● Automated implementation of new software.
● Helpful hand-holding for first-time users.
Amazon Web Services

AWS is an Amazon Joint Venture offering on-demand, metered pay-as-you-go applications for individuals, businesses, and governments with Cloud Platforms and APIs. The cloud computing web services provide a selection of simple abstract technical infrastructures and distributed components and software. Amazon Elastic Computing Cloud (EC2), a virtual machine cluster that is always online, is one of these facilities. The AWS edition of virtual machines emulates many of the computer’s basic features such as the leading hardware processors and processor modules for computer local / RAM processing and harddisk / SSD storage, the selection of operating systems, and networking. AWS is compatible with the operating systems.
Become among the certified AWS professional placed at major IT giants across the globe with the help of AWS Online Training.
Features of AWS
● Flexibility
● Cost-effective
● Scalable and elastic
● Secure
● Experienced
What does AWS do?
Amazon Web Services ( AWS) is a reliable cloud services platform providing computing resources, database storage, content distribution, and other capabilities to help companies expand and scale. Simply put, AWS lets you do the following things-running web and application servers in the cloud to host dynamic websites.|
Advantages of AWS
● AWS has better availability
● Storage is the best feature provided by AWS.
● Databases, data processing is easy to do with AWS.
● Hybrid cloud and migration is also a feature that makes AWS more appealing and provides many advantages.
● Networking with AWS becomes simpler.
● AWS is helping a lot of tools to develop
● Management and control of AWS are easy to handle and very useful.
● AWS Governance and Confidentiality is the most critical aspect of ensuring data security
● Control and Analysis of Big Data with AWS are effectively done.
● AWS is commonly used in Artificial Intelligence and has provided AI with futuristic technologies and made many things possible.
Join our job-oriented and well-researched AWS Training in Pune.
Microsoft’s Azure

Microsoft Azure is a cloud service developed by Microsoft to build, test, deploy, and manage software and services through Microsoft’s data centers. It offers business software (SaaS), a service platform (PaaS), and service infrastructure (IaaS). It supports several programming languages, tools, and frameworks, including both Microsoft and third-party software.
In October 2008, Azure was unveiled and introduced with the code name “Project Red Dog” and released as Windows Azure on 1 February 2010 before being renamed Microsoft Azure on 25 March 2014.
AWS, Salesforce, Hadoop, IBM Bluemix, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure are the few cloud service providers/platforms that are commonly used and in demand. If you are a licensed professional on these channels, you need a high need on the market. You will have countless prospects in the IT sector and are eligible for high paying job profiles.
Features of Microsoft Azure
● A quick method of registration
● Easy billing per hour
● AWS Comprises three essential foundations of cloud computing
● Omnipresence
● Scalability and elasticity:
● Flexibility
● Great deal with Amazon services
● Stability and Trusted Vendors
● Quick Learning & Certification
How does Microsoft Azure work?
Azure is a cloud platform for Microsoft. Azure provided a wide variety of services, including service framework (PaaS), service infrastructure (IaaS), and managed database service capabilities.
Like other cloud services, Azure relies on a technology known as virtualization. Most computer hardware can be emulated in software because most computer hardware is simply a set of permanently or semi-permanently encoded in silicone. Using an emulation layer that maps software instructions to hardware instructions, virtualized hardware will run in software as if it were the hardware itself.
Essentially, the cloud is a group of physical servers in one or more data centers that run virtualized hardware on behalf of customers.
Unblock your career with the trending Azure DevOps AZ 400 Certification.
What Are the Career Paths of a Cloud Computing Engineer?

The growth of the cloud as a significant IT variable for many companies has led to a significant increase in demand for all forms of cloud computing skills. Cloud engineer, a core member of any cloud computing team, is one of the fastest-growing jobs.
Since the move to the cloud was so abrupt and all-encompassing, it left many businesses with a skills gap that they’re struggling to fill with professionals with cloud expertise. This includes the position of cloud engineer.
This demand for cloud computing has led to the need for more jobs in cloud computing. The three top five places were cloud protection, cloud architecture, and cloud engineer.
The firm said that the conventional IT positions that can be converted into cloud professions include system engineers, network engineers, and database administrators.
Cloud engineers are responsible for various technical aspects of cloud computing technology and techniques. Their roles may include planning, overseeing, maintaining, and promoting cloud projects in collaboration with other team members, such as cloud architects and security engineers.
Many cloud engineers are interested in network architecture, data storage, virtual machine (VM) resource allocation, cybersecurity, and other fields. Someone in this role can take on many of these tasks or only concentrate on one or two, depending on the organization’s size and the nature of the cloud initiative.
Given the potential spectrum of roles, cloud engineers should be familiar with cloud service offerings and environments from major cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Google, and others. They will need to have a strong understanding of software development, systems engineering, web services, and a range of programming languages.
Cloud Computing Career Roadmap includes the below job profile.
● Cloud Solution Architect
● Cloud Developer Engineer/ Cloud Software Engineer
● Cloud DevOps Engineer
● Cloud System Engineer/ Administrator
● Cloud SysOps Administrator
● Cloud Network Engineer
● Cloud Network Security Engineer
● Cloud Product Manager
● Cloud Consultant
Benefits of Cloud Computing
All this seems like there is no better time to get your head into the cloud because of the clear directions in which the industry is advancing.
Cloud computing has become a popular concept. As the data usage has risen dramatically, which has driven society to a digital 21 st century transition, the maintenance of all sensitive information, services, and systems on in-house database servers is becoming increasingly difficult for individuals and organizations. The problem is solved almost as long as the Internet has been around, but it has only recently earned widespread implementation for enterprises.
The benefits or advantages of cloud computing are as follows.
● Cloud computing is significant cost savings.
● Security-wise, the cloud gives complete assurance.
● Cloud computing is very flexible.
● It gives mobility
● The practical and best insight it offers
● Cloud computing has increased collaboration.
● Good quality control
● Disaster Recovery is very efficient.
● It prevents losses
● It automatically updates software.
● It has a competitive edge.
● Sustainability is excellent
Update your skills with DevOps AWS Training
Major Cloud Computing Roles
All this seems like there is not a be building a cloud takes a team. Here are the positions of the cloud leaders of today and tomorrow, who lead the cloud revolution in their companies:
CIOs, CTOs, IT representatives, and IT experts. Even if a company is in the cloud , experienced administrators and experts would also need to consider the best options for their companies.
Sales and marketing managers. They are at the forefront of businesses and are now voracious consumers of applications like Salesforce. They feel the pinch of the global economy directly and want quick, easy-to-learn solutions. It’s all-time to sell.tter time to get your head into the cloud because of the obvious directions in which the industry is advancing.
Cloud computing has become a popular concept. As the data usage has risen dramatically, which has driven society to a digital 21 st century transition, the maintenance of all sensitive information, services, and systems on in-house database servers is becoming increasingly difficult for individuals and organizations. The problem is solved almost as long as the Internet has been around, but it has only recently earned widespread implementation for enterprises.
Security managers. Knowledge of security protocols is essential regardless of the type of cloud that is used. This includes an interpretation of mandates and laws – such as Sarbanes-Oxley, HIPAA, and the endless data-processing legislation in countries within the United States from the European Union.
Analysts and data managers. Authorized data requires accuracy and timeliness to provide details on which to base the business decision. Can cloud-based systems mesh data with ERP, data warehouse, or other systems seamlessly? Does it produce data? Data practitioners and designers may use the cloud to create systems capable of ingesting Big Data from the cloud or providing analytical environments.
Architects, designers, and analysts of firms. These people are necessary to draw up a road map of which services are available – whether from IT or an external provider. They can work with the corporation, speak the business language, and work with IT specialists.
Managers of procurement or purchasing. Cloud renders vendors pervasive in a day-to-day company, making it a must for people who train or know how to negotiate with vendors. People need to collaborate with cloud providers and discuss deals at the service level, accessibility. You must read the fine print in the contracts between suppliers and call the carpet if things aren’t as expected. These people will step up to the challenge and make the right noise when a cloud service falls or typically goes under.
HR Managers. The ability to manage cloud environments, from building solutions to data integration to operational management, requires that talent with the right skills can be found, hired, and educated.
CEOs and CFOs, as well as other C-level executives. These are the people with whatever significant cloud movements must be on board.
Employees at every stage. Cloud computing systems enable and offer various online efficiency and co-operation systems to all levels of organizations. Employees know the resources they need to assist them in their work and meet their clients. The decisions made by the cloud — and acceptability — successfully or fail to take up service by employees.
If you want to know more about Cloud Computing Courses, do check 3RI Technologies
Steps to Become a Cloud Engineer

Stepwise
The process to become a cloud engineer
Step 1: Cloud computing platform skills increase
In at least one of three leading cloud platforms — AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud (GCP)—the primary and foremost way to become a Cloud engineering engineer. Many tools, such as YouTube videos, educational papers, and virtual or physical training, can be found on the internet to obtain a superficial understanding. If you have achieved this in any of the respective environments, you will continue to be accredited.
AWS can be classified into four categories into separate certifications:
Foundation (basic)
Associate
Professional
Specialty-level
In the same way, there are numerous training routes and certificates for Azure, as seen in the following graphics:
The majority of cloud providers also have a free service level. This is particularly useful when deciding to migrate to — or if you want to shift your workloads to more than one cloud depending on your company requirements and ROIs.
Step 2: Getting expertise in the least language
Cloud computing includes other data-based programming languages like Python, Java, and Clojure, unlike general programming languages like C and C++. You can use journals, videos, online/offline courses, and other free tools to learn these things.
Step 3: Specialization
As well as acquiring expertise and being trained with at least a programming language in the cloud computing systems, you need to understand key concepts such as:
Networking and Storage
You need to know how to store the data and where to access it with the storage. It is also critical that you have some experience with the Azure and AWS services, such as the Microsoft Azure S3 and Azure Storage. You must even grasp the basic principles of networking strongly.
Check out Azure Training in Pune
Operating and Virtualization Framework
During physical infrastructure usage in cloud data centers, virtual machines ( VMs) that work on the hardware are most critical in configuring and maintaining them. You must also know how these VMs operate on virtual cloud networks. Public clouds are also OS-agnostic, so Windows and Linux operating systems can be easily understood.
Disaster Recovery and Security
Cybersecurity threats and malicious attacks must protect data, applications, and infrastructure. By ensuring that your systems are secure and continuously backed up to avoid any data loss, you should be ready for any unforeseen occurrence.
DevOps and Web Services
Are you well aware of how cloud computing can provide a centralized platform for research, deployment, and manufacturing DevOps automation? Also, are you aware that the operations and production teams need coordination with DevOps? This is a must in today’s agile and dynamic environment.
Cloud Engineer Salary

Salary of the cloud engineer
Cloud developers are now earning high wages. According to Payscale, they receive around $116,800 a year in the United States, and in India, they pay about $6,66,800 a cloud engineer per year. Indeed, the more cloud computing experience you obtain, the better chance you can earn a higher wage.
An IDC study states that public cloud services and storage prices will be twice as high as they are now at the end of 2023. by 2023. The amount is enormous! No wonder the average pay of cloud engineers is expected to increase!
Some salary patterns give you a clear picture of the future of cloud engineers:
In Gartner’s report, the cloud engineers’ average salary was 146,530 dollars in 2018, while it only amounted to 124,300 dollars two years ago, in 2016. A little over $22,000! This is a leap!
By 2020, the cloud will store 83 percent of company workloads.
Types of Cloud Computing
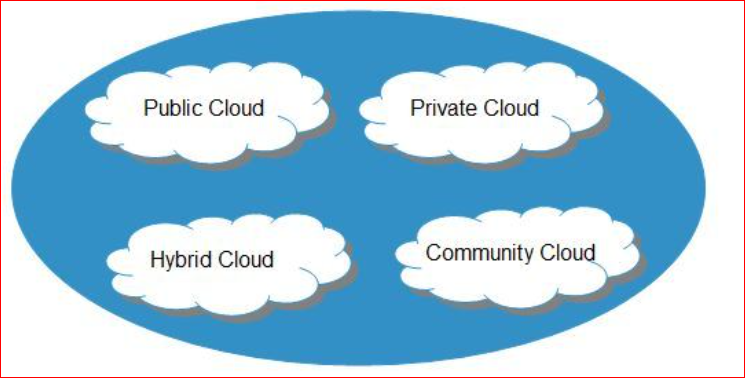
The two types of Cloud Computing which are:
Deployment Model
Service Model
The following forms of cloud computing may be available based on the three styles of deployment model:
Public
Community Cloud
Private
Hybrid
Public Cloud
The public cloud is defined as a computing service offered via the public internet by third-party providers, making it available to those who choose to use or purchase it. It may be free or on-demand for consumers to pay for the loops, storage, or bandwidth they use.
Example: Sun Cloud, AWS, Azure,
Community Cloud
Only cloud technology may be used by a particular community of clients from organizations with everyday issues. It may be owned, controlled, regulated, and administered by one or more communal organizations, a third party, or a combination of them.
Private cloud
A private cloud is a cloud storage system where IT services are offered for the specialized use of one entity over private IT facilities. The cloud infrastructure is managed by a single company only. It can be controlled on-site or off-site by a company or a third party. Private cloud terms are also used interchangeably with virtual private clouds (VPCs). Technically speaking, a VPC is a private cloud that uses a third-party cloud provider’s resources while an internal cloud is being introduced.
Example: VMware, AWS
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines a government and a private cloud to share information and apps. Organizations gain versatility and government cloud computing capabilities for key and insensitive computing tasks while remaining protected behind a corporate firewall for business-critical apps and details.
Cloud Categories Based on Service Models
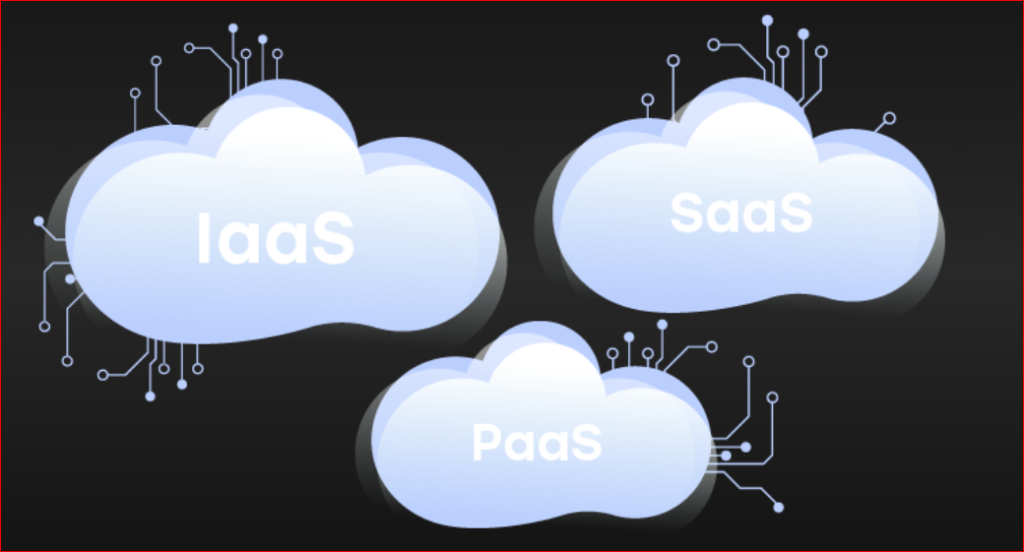
While the development of cloud computing has been substantially divided into three large service categories:
- Service Infrastructure(IAAS)
- Service Software (PAAS)
- Service Software(SAAS)
Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS)
Service infrastructure (IAAS) offers virtualized computer services on the Internet. It is a type of cloud computing. A third party vendor hosts on behalf of its user’s hardware, software, servers, storage and other infrastructure components in an IAAS model. IAAS providers also host user applications and perform systems support and resilience preparation activities.
IAAS systems provide highly flexible, on-demand adjustable services that are ideal for temporary, creative and volatile working charges. The automated management, dynamic scaling, virtualization on the desktop and political services are other features of IAAS environments. Other IAAS features include administrative task automation, dynamic scaling, virtualization on the cloud and political services.
IAAS-Network:
Public Cloud service providers provide two primary network services: load balance and DNS. Load balancing provides a single access point to several servers running behind it. A load balancer is a network system that distributes net traffic through the servers using complex algorithms for load balancing. DNS is a computer hierarchical naming scheme or some other gaming device with network identification IP addressing – a DNS system blends IP addresses with domain names.
Platform As A Service (PAAS)
Platform as a service (PAAS) is an Internet-based cloud computing model. In a PAAS model, a cloud provider provides its users with software and software tools, ushering in applications. A PAAS provider hosts its infrastructure for hardware and applications. As a result, PAAS frees users from the need to develop or operate a new application by installing in-house hardware and software.
PAAS does not replace the whole infrastructure of a company but relies instead on key resources such as Java creation or application hosting from PAAS providers. However, a PAAS provider supports both underlying software and computing; users typically can only log in and start using the platform through a Web browser interface. For this access, PAAS providers would then charge per user or monthly.
Software As A Service (SAAS)
Software as a Service(SAAS) is a model for software delivery that hosts applications by vendors or service providers and makes users, usually on the Internet, accessible on a network. SAAS has become an increasingly commonly used delivery model as technologies underlying the mature and common approaches to new development such as Ajax support Web services and service-oriented architecture (SOA). SAAS has strong ties with models of on-demand device delivery for ASP (Application Service Provider). IDC defines the host application model and software development model for two slightly different SAAS delivery models.
Storage As A Service (SAAS)
Storage as a service is a business model in which a big company leases room for a smaller company or entity in its storage infrastructure. In principle, the economy in size in the facilities of the service provider makes it far more cost-effective for them to provide storage than other people or businesses would store themselves if they consider the overall cost of ownership. Storage as a service is typically considered a suitable alternative to implementing and maintaining its storage infrastructures for a small or medium-sized enterprise that lacks the financial resources and technical staff.
Communications As A Service ( CAAS)
CAAS is an outsourced messaging service for businesses which can be rented from a single supplier. These communications may include voice over IP, instant messaging (IM) and collaboration applications, and the use of mobile and fixed devices. The CAAS vendor handles both hardware and software and provides quality of service ( QoS) guaranteed. CAAS helps organizations to choose the appropriate pay-as-you-go communications devices and methods.
Network As A Service (NAAS)
Network as a Service (NAAS), a system that combines existing cloud services with direct yet secure customer access. NAAS is a modern paradigm for cloud computing where consumers have access to external computer services with switches and routers. NAAS provides versatile and expanded Virtual Private Network ( VPN), on-demand bandwidth, customizable routing, multicast protocols, security firewalls, intrusion detection, WAN, content control and filtering and antiviral systems.
Monitoring As A Service (MAAS)
Monitoring as a service ( MAAS) is a platform that makes it easier to deploy monitoring functionality for a range of other cloud-based services and applications. MAAS ‘most frequently used application is online monitoring of state, which continuously track such processes, networks, structures, instances or elements that can be deployed in the cloud. MAAS enables the implementation of state surveillance at various levels of cloud services for consumers.
Who Uses Cloud Services?

Sounds like a technical term for cloud computing, which is why people consider it something “experts” only use. The truth is that cloud computing virtually stores, manages and handles data through the Internet and almost everyone with experience in accessing or uploading online files tasted the cloud computing.
So who uses cloud computing on a more comprehensive level? Here are some of the groups that are using cloud computing and using the cloud for:
Small company owners – Small businesses can save storage space and manage their stored information more effectively through cloud computing. They can opt instead for cloud storage services and also reduce costs rather than providing a storeroom that uses electricity and space.
Larger companies – cloud storage companies benefit from another disaster recovery step in their central archives. Big companies typically have their file saving methods, but when it comes to backups, they often use cloud computing to have extra protection. Cloud storage also allows both small and large organizations access to files, even though they are out of the workspace. This makes it possible for large corporations with an eye to expansion to share such information with other potential partners by enabling their cloud access. This makes it easier for them to share details.
The industry that manages hundreds of customer files – health care, schools, property and the like – is also entitled to benefit from the cloud, as they may provide hundreds or even thousands of different customers’ digital backups. Cloud services are available that can update entries simultaneously and conveniently reference files. This helps shorten the time it takes to search customer files which the service provider wants to access.
Personal users – Cloud computing users may also be ordinary people. Can this make it easier for individual users to share files, or for personal file storage, by saving space on their hardware and storing their files online. It won’t be easy to save and access files so long as there is internet access, so the user can be sure the files are cloud safe.
Depending on who is using the cloud, there are individual variations in how the cloud is used. However, despite these differences, it is sure that this technology enables file storage, management and recovery to be more effective. There are often people who use the cloud to store digital information in a secure environment, whether it is paying for or free cloud storage.
Cloud engineer skills
Cloud computing sounds bright, fluffy and like a rainbow to people who are outside. Cloud computing, however, is too profound and sophisticated and requires engineers to be technologically experienced.
You may already have many of the abilities you need to succeed in the cloud if you are an experienced engineer in a different discipline. And as the cloud is very new, you can differentiate yourself by applying what you know to learn quickly.
You must understand the ins and outs of building and running applications in the cloud as a cloud engineer. While programming and scripting experience usually is required for this role, the particular language conditions are much more comfortable than in conventional engineering employment.
What skills do you need?
- AWS, Azure, OpenStack, Microsoft.At least one of these should be known to you. If in one stack you are well versed in this information, the design of software for the other stacks is reasonably straightforward. That will mean learning a little at work to make it successful.
- Web Services, APIs, REST, RPCs. APIs and Web Services are the pillars behind the cloud infrastructure. You probably already have experience in working on websites with specific service patterns, protocols, and this information gives you a start to mastering the fundamental concepts of the cloud.
- Virtualization, Computing, Internet access. These skills can be instrumental in the field of cloud computing for design and service. This is a positive thing if you have those skills! You should at least have a good history in programming because the learning curve will be a little too steep without it.
- High availability, failure over, redundancy and disaster recovery. These are methods which are fundamental to the operation of cloud computing and are competences you usually have in an operational role. What if you didn’t do previous operations? As long as you know these principles, you can learn the pieces related to cloud architecture with some experience and workplace preparation.
Get certified in Cloud Computing with Amazon Web Services Course at 3RI Technologies.



